1. Introduction to Copper Tube Busbars
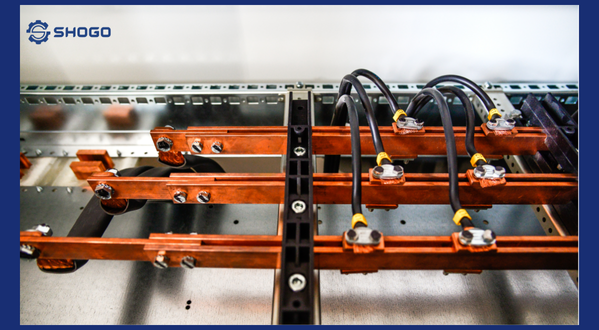
Definition: A copper tube busbar is an electrical conductor made from pure copper, shaped into a circular tube. Due to their exceptional conductivity and durability, they are widely used in industrial electrical systems and electronic devices.
Comparison: Compared to other types of conductors like flat copper bars and aluminum bars, copper tube busbars offer several advantages:
- Conductivity: Copper has higher conductivity than aluminum, reducing energy losses during transmission.
- Heat resistance: Copper tube busbars have better heat resistance, making them suitable for high-temperature environments.
- Mechanical strength: Copper tube busbars have high mechanical strength, capable of withstanding strong mechanical impacts.
- Flexibility: The circular shape makes copper tube busbars easy to bend and install in confined spaces. Applications:
- Industrial electrical systems: Copper tube busbars are used as busbars in distribution panels, electrical substations, manufacturing plants, etc.
- Electronic devices: Copper tube busbars are used in high-power electronic devices such as inverters, UPS, etc.
- Other industries: Oil and gas, chemicals, renewable energy, etc.

2. Structure and Operating Principle
Structure:
- Material: High-purity pure copper.
- Shape: Circular tube with various sizes depending on the application.
- Joints: Joints are usually made by welding or pressing.
- Operating principle:
- Current conduction: The current flows along the inner surface of the copper tube.
- Current distribution: The copper tube busbar distributes the current evenly to the consuming devices.
- Load bearing: Thanks to its large cross-sectional area, the copper tube busbar can withstand high currents and temperatures without damage.
3. Manufacturing Process
Stages:
- Material selection: Selecting high-purity pure copper.
- Tube processing: Copper tubes are produced by drawing or extrusion.
- Welding joints: Tube sections are welded together to form a copper tube busbar of the desired length.
- Quality inspection: Checking technical parameters such as diameter, thickness, and surface smoothness.
- Quality standards: Copper tube busbars must meet international and industry standards for conductivity, mechanical strength, heat resistance, etc
4. Applications of Copper Tubular Busbars in Practice

Specific examples:
- Electrical distribution systems: Copper tubular busbars are used as busbars in electrical distribution panels to distribute power to consuming devices in factories and buildings.
- Substations: Copper tubular busbars are used to connect equipment in substations, ensuring efficient energy transmission.
- Electrical equipment: Copper tubular busbars are used as conductors in inverters and UPS systems to supply power to electronic devices.
5. Selection and Use of Copper Tubular Busbars
Factors to consider:
- Rated current: Select a busbar with a cross-sectional area suitable for the system’s rated current.
- Rated voltage: Ensure the busbar can withstand the system’s operating voltage.
- Operating temperature: Choose a busbar with good heat resistance in the working environment.
- Operating environment: Determine the working environment to select the appropriate type of busbar (indoor, outdoor, harsh environments).
Safety standards:
- Installation: Adhere to installation regulations to ensure electrical safety.
- Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance to extend the busbar’s lifespan.
- Electrical safety: Always follow electrical safety rules when working with copper tubular busbars.
6. Advantages, Disadvantages, and Comparison
Advantages:
- High electrical conductivity
- Excellent heat resistance
- High mechanical strength
- Flexibility
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to other types of conductors.
- More difficult to process than some other types of bars.
7. Development Trends and Future Prospects
New technology: The trend is to develop copper tubular busbars with higher purity and better heat resistance.
Applications: Copper tubular busbars will be more widely applied in new industries such as renewable energy and electric vehicles.