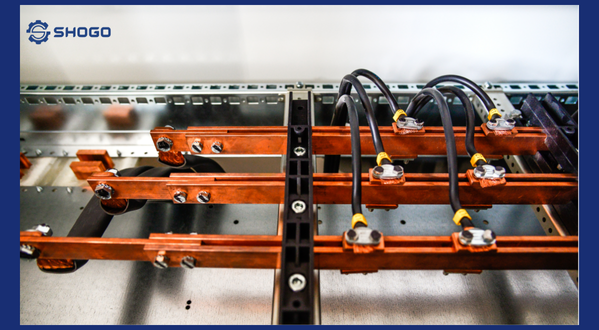
1. Introduction
A busbar is an essential component in electrical systems, serving as a conductor to create electrical connections and distribute power. Tin plating involves coating a busbar with a thin layer of tin. This tin coating protects the busbar from oxidation and corrosion, enhancing its conductivity.
Typically made of copper or aluminum, tin-plated busbars have a tin layer varying in thickness from a few to several tens of micrometers, depending on specific requirements. They are classified based on shape (round, square, rectangular), size, and application.

2. Reasons for Using Tin-Plated Busbars
Tin offers several advantages, including excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, high ductility, easy processing, and an aesthetically pleasing appearance. These properties make tin-plated busbars superior to unplated ones:
- Increased lifespan: The tin coating protects the busbar from environmental factors, extending its service life.
- Enhanced stability: It ensures stable electrical system operation, minimizing failures.
- Reduced risks: It lowers the risk of fires caused by poor connections.
- Improved aesthetics: Tin-plated busbars have a shiny, attractive finish.
3. Manufacturing Process
The production process involves:
- Material preparation: Selecting suitable materials (copper or aluminum) and plating chemicals.
- Busbar processing: Shaping the busbars to the desired dimensions.
- Surface cleaning: Thoroughly cleaning the busbar surface for optimal coating adhesion.
- Tin plating: Applying tin using methods like electroplating, hot-dip plating, or spray plating.
- Quality inspection: Verifying coating thickness, adhesion, conductivity, and other properties.
4. Applications
Tin-plated busbars find extensive use in:
- Electrical industry: Electrical panels, switchboards, household appliances, and industrial power systems.
- Other industries: Electronics, automotive, and aerospace.
5. Standards and Quality
Tin-plated busbars must meet quality standards, including:
- Coating thickness: Ensuring the coating meets specified thickness requirements.
- Adhesion: The coating must adhere firmly to the busbar surface.
- Conductivity: Ensuring excellent conductivity.
- Mechanical strength: Ensuring sufficient strength to withstand operational stresses.
6. Considerations for Use
- Storage: Avoid exposure to chemicals and strong impacts.
- Cleaning: Regular cleaning is essential for optimal performance.
- Repair: Damaged busbars should be repaired or replaced promptly.
7. Future Trends
- New plating technologies: Development of advanced plating techniques like vacuum plating and ion plating for improved coating quality.
- Alternative materials: Research into new alloys to replace copper and aluminum.
- New applications: Expanding the use of tin-plated busbars in smart electronic devices and renewable energy systems.
Conclusion
Tin-plated busbars are crucial components in the electrical industry. Their superior properties and wide range of applications make them a preferred choice. Ongoing advancements in materials and manufacturing processes will further enhance their performance and expand their use.